About technology
3D printing has proven its effectiveness in a great number of industries. It is used for the production of small batches of products of complex geometry, spare parts and cutting-edge equipment.
However, it is yet a highly innovative technology with limitless potential.

Additive Technology
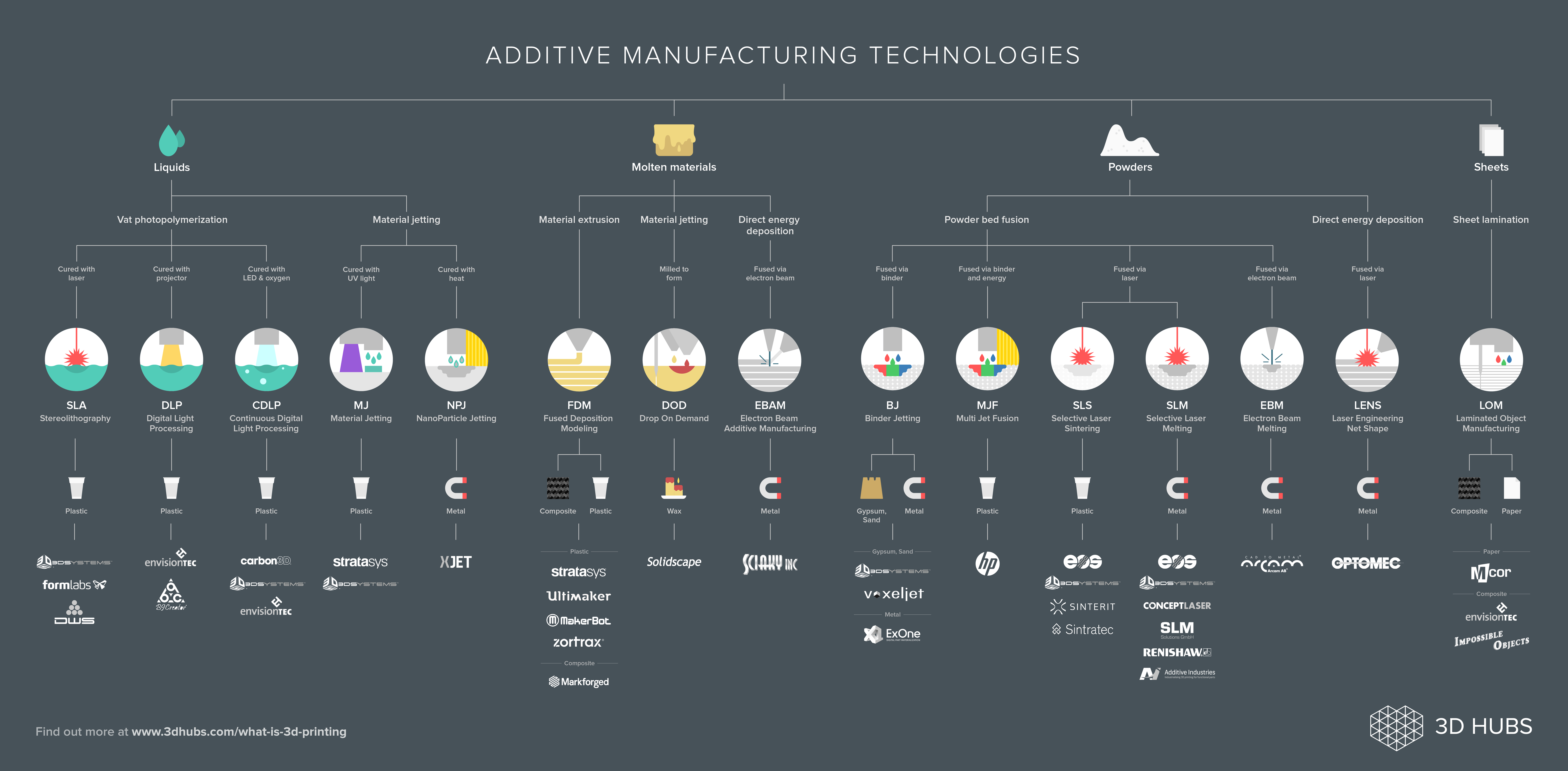
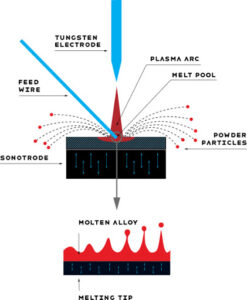
Additive technology, or 3D printing, is a term covering more than 20 different methods for layer-by-layer building and synthesis of objects. The most common ones are LBPF, FDM, SLA/DLP.
These methods use different input materials (plastic, metal, composites) in different states (powder, thread, liquid) and different sources for their synthesis and formation (laser, light-emitting diode, electron beam, heating nozzle).
It’s worth mentioning that each method is specific in its own way, has own pros and cons. A common concept of technology is what unites all of them. The process begins with 3D modeling of the object to be obtained in the CAD system; then the 3D object is exported to the CAE system, where it is layered and then these layers are divided into individual tracks with the preset parameters (for instance: beam speed, beam power, laser spot size, etc.); this information is transmitted to the printing device sequentially executing the set commands.
Pros of 3D printing
Additive technologies provide lots of advanced features in the production cycle:
- prompt receipt of a prototype or sample;
- production of complex-geometry products;
- a reduction in numbers of technological operations in order to obtain products;
- enhanced products efficiency;
- production waste reduction.
In order to be able to apply the Technology, it is necessary to consider the specific features of each printing method.
Technologies are highly effective for small batches and complex-geometry components.